Key Takeaways
- SAP regression testing verifies existing system functionality after changes, serving as a safety net since modules like FICO, MM, SD, and PP are deeply integrated with shared data and workflows.
- Organizations with mature regression testing practices report higher user satisfaction, lower defect rates, and faster release cycles while maintaining compliance with standards like SOX and GDPR.
- The average critical ERP outage costs companies $4.88 million, making regression testing not just a quality gate but financial insurance against production disruptions.
- Test automation is essential for SAP regression at scale, with enterprises implementing it achieving 548% ROI over five years and a typical payback period of just seven months.
- Risk-based testing focuses efforts on high-impact areas like financial postings and integration interfaces, maximizing defect detection by assigning risk scores based on business criticality and change frequency.
Skip regression testing and you’re gambling with production stability. Companies like Shiseido reduced testing time by 85% while catching nearly all defects before production. Discover how to build an effective SAP testing strategy that pays for itself 👇
What is Regression Testing in SAP?
Regression testing in SAP verifies that your system still works after changes. Applying patches. Rolling out enhancements. Migrating to S/4HANA. Deploying custom code. Pushing configuration updates through transports. You’re re-running tests on existing functionality to catch unintended side effects before they hit production.
SAP regression testing is essential because SAP systems are deeply integrated. Modules like FICO, MM, SD, and PP don’t exist in isolation. They’re wired together, sharing data and triggering workflows across boundaries. A pricing rule change in Sales & Distribution might affect how invoices post in Finance. A new field in Materials Management master data could break custom reports in Production Planning.
Real-world example: You update your tax calculation procedure in FICO. You run transaction FB60 to post a vendor invoice. Everything looks fine. Three days later, your month-end close fails because automated tax postings aren’t flowing to the right GL accounts. That’s a regression. The update didn’t break the invoice posting itself. It broke something downstream that depended on how tax calculations worked before.
Regression testing catches these scenarios by re-validating critical business processes after every change. It’s not about testing new features. That’s functional testing. It’s about making sure the stuff that worked yesterday still works today. This becomes especially critical during major transitions like S/4HANA migrations or ERP system migrations where legacy processes, custom Z-reports, and Fiori applications all need validation.
When regression testing is essential:
- System patches and support packs
- Transport deployments moving changes across landscapes
- Custom development touching core modules
- Configuration changes affecting business processes
- Data migrations or conversions
- Integration updates between SAP and external systems
Each of these represents a potential point of failure. Skip regression testing on any of them and you’re gambling with production stability.
In SAP regression testing, having the right tools can significantly reduce your testing burden. aqua cloud offers a comprehensive test management solution that addresses the exact challenges highlighted in SAP environments. With aqua’s risk-based testing approach, you can prioritize critical business processes like order-to-cash and financial close procedures, focusing your testing efforts where they matter most. The platform’s centralized test repository ensures all your SAP test assets remain organized and reusable and cuts maintenance overhead by up to 70% compared to manual approaches. Now enhanced with aqua’s domain-trained AI Copilot, you can automatically generate regression test cases from your SAP requirements and accelerate test design while maintaining project-specific context and accuracy.
Generate comprehensive, risk-prioritized SAP regression suites in minutes instead of weeks with aqua cloud
Importance of SAP Regression Testing
Skip regression testing and production breaks. The average critical ERP outage costs companies $4.88 million. One bad release wipes out quarters of budget in downtime, emergency fixes, and lost productivity. SAP regression testing is financial insurance.
Your SAP environment runs interconnected business processes spanning departments, geographies, and systems. Change one piece and you potentially affect dozens of downstream workflows. Regression testing safeguards these connections by validating that updates don’t introduce defects.
Compliance matters. In financial services, healthcare, or any regulated industry, your SAP processes need to meet standards like SOX, GDPR, or industry-specific regulations. Break an audit trail in a regression? You’re looking at penalties. Mess up data handling procedures? Failed audits. Bypass authorization controls? Regulatory scrutiny. Your regression suite should validate compliance requirements alongside functional processes. Make sure SOX controls still fire. GDPR data masking still works. Authorization objects haven’t been bypassed.
User experience impacts adoption. When business users encounter broken processes after an update, confidence erodes fast. They start questioning every change. They resist new features. They build shadow workarounds that introduce more risk. A robust regression testing approach builds trust. Updates won’t disrupt daily work. This creates a foundation for continuous improvement. Teams can push enhancements knowing existing functionality won’t regress.
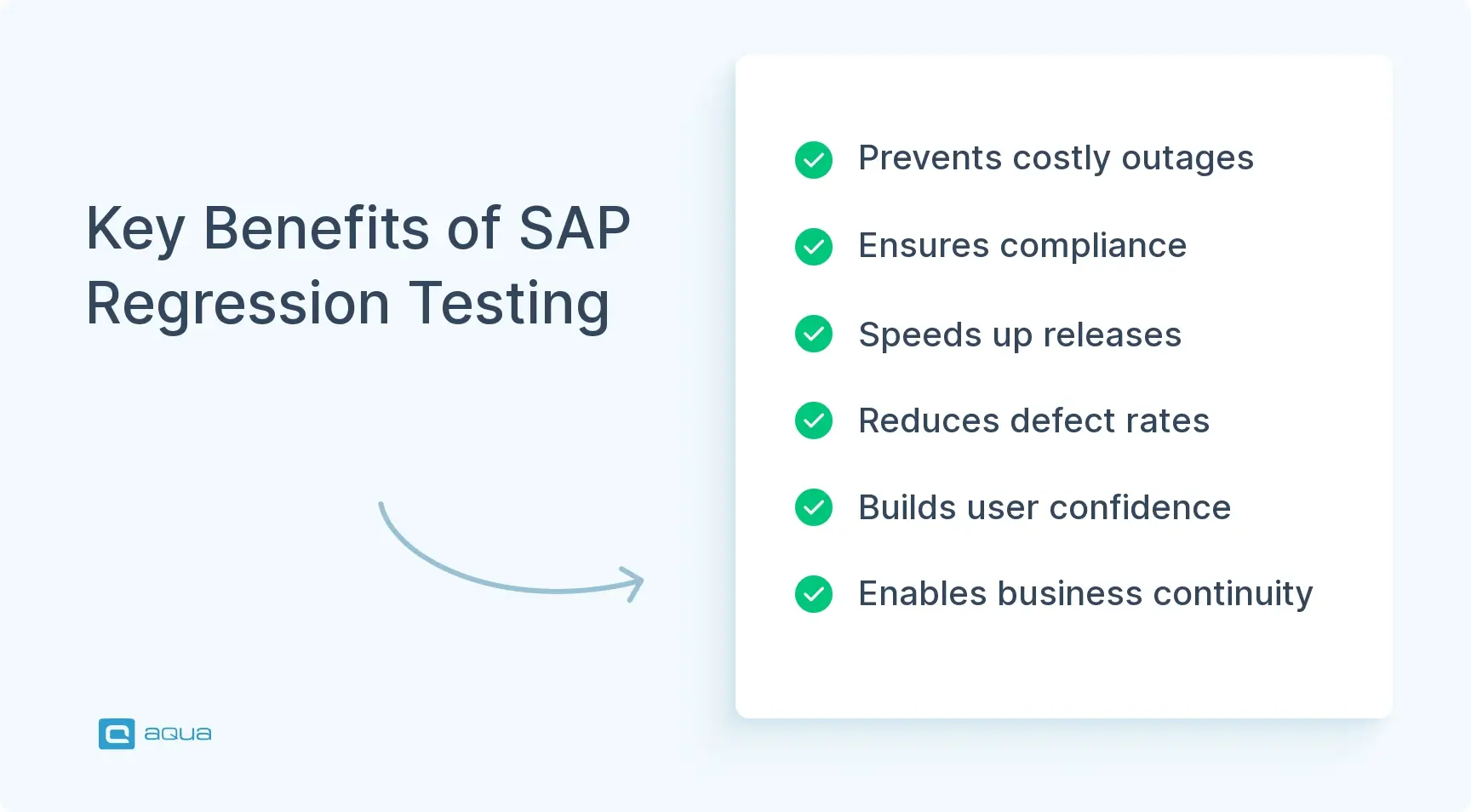
What regression testing delivers:
- Business continuity – Critical order-to-cash, procure-to-pay, and record-to-report processes keep running
- Compliance assurance – Regulatory controls remain intact across updates and migrations
- Cost avoidance – Catching defects in testing costs a fraction of fixing them in production
- Release velocity – Automated regression suites enable faster, more frequent deployments
- Risk mitigation – Integration points between modules are validated, preventing cascading failures
- Stakeholder confidence – Business users trust that updates won’t break their workflows
If you invest in comprehensive SAP regression testing solutions, you can position yourself to innovate faster while maintaining stability. But getting there requires overcoming significant challenges.
SAP Regression Testing Challenges & How to Overcome Them
Regression testing in SAP is brutal work without the right approach. The scale and complexity of enterprise SAP landscapes bog down testing cycles, consume resources, and leave coverage gaps that haunt you in production. Understanding these pain points is the first step toward solving them.
Resource Demands
There’s a documented shortage of SAP testing expertise. Your QA teams scramble to find people who understand module interdependencies, custom code impacts, and integration nuances. Many teams burn 30-50% of their testing time just on environment setup and data management. Before they’ve run a single test. This bottleneck contributes to the 74% of SAP projects that experience delays.
Without specialized skills, your testers struggle to identify which business processes need validation after changes. You end up over-testing (wasting time) or under-testing (missing critical scenarios). The fix? Prioritize automation tools that reduce dependency on scarce technical expertise. Invest in cross-training to build internal capability across functional and technical testing domains.
Long Testing Cycles
Traditional regression testing in SAP means your testers manually execute test scripts through SAP GUI. This can take weeks or even months for comprehensive coverage. That timeline doesn’t fit modern business demands for rapid updates and quarterly cloud releases. Long testing cycles delay critical deployments. You create backlogs of changes waiting for validation. You can’t keep pace with innovation or competitive pressure.
Automation is the only viable path forward. But you need to be strategic about what you automate. Focus on high-value, repeatable scenarios. Core business processes. Integration points. Frequently-run tests. Save manual testing for exploratory work, unstable UI flows, and one-off validations.
Coverage Gaps
SAP systems have so many integration points and custom configurations that ensuring comprehensive testing without automation is nearly impossible. Your teams often focus on obvious, high-visibility processes while missing critical edge cases or module-to-module dependencies. A change to invoice posting might get tested in Finance. But does your suite validate how it affects Controlling, Materials Management inventory valuation, and Sales & Distribution revenue recognition? These blind spots lead to production defects you could’ve caught with broader test coverage.
Overcome this by implementing risk-based testing that prioritizes based on business impact and change likelihood. Maintain a living test repository that evolves with your system.
Core challenges and consequences:
- Skills gap – Lack of SAP testing expertise leads to inefficient test design and execution
- Environment complexity – Creating production-like test environments consumes enormous time and resources
- Data inconsistency – Test data misalignment across modules causes false failures and masks real defects
- Customization density – Standard test cases don’t account for Z-reports, enhancements, and bespoke workflows
- Integration blind spots – Module interdependencies create cascading impacts that manual testing misses
- Automation debt – Legacy test scripts become brittle and require constant maintenance
The path through these challenges involves strategic automation, risk-based prioritization, effective test data management, and continuous improvement of your regression test suite. Organizations that tackle these obstacles see dramatic reductions in testing time, improved defect detection rates, and faster release cycles. Learn more about regression testing approaches that work.
How to Build a SAP Testing Strategy
A robust testing strategy is your blueprint for managing SAP quality at scale. Without one, you’re flying blind. Reacting to failures instead of preventing them. Over-testing low-risk areas while missing critical gaps. Burning resources on redundant manual work. Your strategy should define scope, prioritize what gets tested, establish automation goals, and set measurable success criteria.
Understand Regression vs. Functional Testing
Functional testing validates that new features work as designed. You’re proving that the stuff you just built does what it’s supposed to do. Regression testing validates that changes didn’t break existing functionality. Both matter, but they serve different purposes and require different approaches. Your regression suite should be stable, repeatable, and focused on business-critical paths that can’t afford to break.
Define Your Scope
You can’t test everything. A comprehensive SAP landscape might have thousands of transactions, custom programs, and integration points. Attempting full coverage on every change would paralyze your release schedule. Instead, conduct thorough change impact analysis to identify which modules, functionalities, and business processes are affected by your update.
SAP Solution Manager 7.2 includes tools like Business Process Change Analyzer (BPCA) and Scope and Effort Analyzer (SEA) that automatically determine test scope for each affected business process. These tools can reduce test scope significantly by identifying only the critical paths impacted by changes.
Without Solution Manager, trace dependencies from the point of change outward. What transactions touch the modified code? What business processes use those transactions? What downstream modules receive data from those processes?
Prioritize Based on Risk
Not all business processes carry equal risk or impact. Your order-to-cash cycle, procure-to-pay workflows, and financial close procedures are mission-critical. Failures here directly affect revenue, vendor relationships, and regulatory compliance. Prioritize regression testing for these high-stakes processes over less critical functions.
Risk-based testing assigns risk scores based on business impact (how bad would failure be?) and change likelihood (how often does this area get modified?). Focus your deepest testing efforts on high-impact, high-change areas. For medium and low-risk zones, lighter coverage or less frequent testing may suffice.
Set Automation Goals
Automation isn’t all-or-nothing. You need clear targets. Which test cases will be automated first? What percentage of your regression suite should be automated within 12 months? What ROI do you expect? Start with the low-hanging fruit: stable, repeatable tests for core business processes that run frequently. These deliver quick wins and build momentum for broader automation.
Avoid automating exploratory tests, frequently-changing UI flows, or one-time scenarios that don’t justify the setup cost. Learn more about building a testing strategy that scales with your SAP environment.
Track Key Performance Indicators
Your approach should define KPIs to track progress and ROI:
- Test coverage percentage – What portion of critical business processes have automated regression coverage?
- Defect detection rate – How many regressions are caught in testing vs. escaping to production?
- Test cycle time – How long does a full regression pass take?
- Automation ROI – Cost savings from reduced manual effort, faster releases, and fewer production defects
- Test execution frequency – How often can you run full regression suites?
Document and Evolve
Document your strategy in a living document that evolves with your SAP landscape. Include testing standards, naming conventions for test cases, guidelines for when to update the regression suite, and governance for who approves changes to the test repository. Bring together SAP developers, QA professionals, business analysts, and process owners. This ensures comprehensive coverage and alignment with business priorities.
A well-designed strategy turns regression testing into an enabler of faster, safer innovation. Explore SAP test management solutions that support your approach.
Key Methods for SAP Regression Testing Enhancement
Once your strategy’s in place, it’s time to optimize execution. The methods you choose determine whether regression testing becomes a streamlined process or a resource-draining nightmare. Three core approaches deliver the biggest impact: test automation, risk-based testing, and maintaining a living test repository.
Test Automation
Test automation is non-negotiable for SAP regression at scale. Manual testing can’t keep pace with frequent system changes, quarterly cloud updates, or the complexity of multi-module end-to-end scenarios. Modern automation tools designed specifically for SAP, like Tricentis Tosca, Worksoft Certify, and Panaya, understand SAP’s architecture. They navigate GUI transactions, Fiori apps, and backend processes without brittle scripts that break on every UI change.
These tools offer codeless or low-code interfaces that let business analysts and testers create complex tests without programming skills. They integrate with CI/CD pipelines, triggering regression suites automatically whenever code commits happen or transports deploy. Parallel execution across modules compresses testing timelines dramatically. Tests that took weeks manually can run in days or hours when automated. Enterprises implementing test automation achieve 548% ROI over five years, with an average payback period of just seven months.
But automation isn’t a silver bullet. You need to be strategic about what you automate and how you maintain it. Focus on:
- Core functionalities
- Repeatable tests
- Integration points
- Data validation workflows
- Cross-module business flows
Avoid automating unstable UI flows, exploratory testing, and one-time scenarios. Implement the Object Repository pattern to separate test logic from UI elements. This makes tests easier to update as your SAP system evolves. Use data-driven testing techniques to parameterize test cases. They can execute with varied input data sets that cover edge cases and business conditions. Self-healing scripts that automatically adapt to UI changes are emerging as a game-changer.
Risk-Based Testing
Risk-based testing focuses your efforts where they’ll have the most impact. Instead of treating all test cases equally, assign risk scores based on business criticality, change frequency, and failure history. High-risk areas, such as financial postings, compliance controls, and integration interfaces, receive deeper coverage and more frequent testing. Medium and low-risk zones receive lighter validation or less frequent regression cycles.
This approach maximizes defect detection with limited resources. It also helps communicate priorities to stakeholders. When testing time is tight, everyone understands why certain areas are being validated while others wait.
Living Test Repository
Your regression suite can’t be static. It needs to evolve with your SAP landscape. Every update, customization, and configuration change should trigger a review of your test repository. Are new test cases needed to cover new functionality? Should obsolete test cases be retired? Do existing tests need updating to reflect changed business processes?
Without this discipline, your regression suite becomes stale. You miss new risks while wasting effort on scenarios that no longer apply. Document test cases clearly with expected outcomes, acceptance criteria, and business context. Use consistent naming conventions to prevent redundancy. Establish governance for who can add, modify, or retire test cases. Schedule regular reviews to keep the repository current.
Additional Enhancement Methods
- Baseline testing – Establish reference standards for application behavior at known good states, then compare future executions against this baseline
- AI-powered test generation – Tools analyze historical data, user behavior, and system logs to generate test cases aligned with real-world usage patterns
- Predictive analytics – Machine learning predicts which tests have the highest probability of uncovering defects
- Continuous testing – Embed regression validation into CI/CD pipelines so tests run automatically with every change
These methods compound when combined. Automated, risk-based regression suites maintained in a living repository and integrated with CI/CD pipelines deliver continuous validation that accelerates release velocity while maintaining quality. Learn more about AI in regression testing and how it transforms test efficiency.
Impact of Effective Regression Testing
When you get regression testing right, the business impact is substantial and measurable. Here are real-world examples that show what’s possible.
Shiseido: S/4HANA Migration
Shiseido, the global beauty and personal care company, faced a massive challenge during their SAP S/4HANA migration. They needed to validate that legacy processes, custom reports, and integrations would continue functioning post-migration. By implementing automated regression testing with targeted impact analysis, Shiseido achieved:
- 85% reduction in testing time
- 99% reduction in defect risk
- 98% reduction in test scope
They compressed months of potential testing work into weeks. They caught nearly every defect before production. They focused effort only where it mattered. This enabled them to complete the migration on schedule while maintaining business continuity.
Boingo Wireless: Oracle Cloud Updates
Boingo Wireless tackled quarterly Oracle Cloud update testing. Before automation, validating updates took 2.5 weeks of intensive manual testing. After implementing automated regression testing, they reduced that timeline to three days. That’s an 88% time reduction. They achieved 80% ROI in just four months. The freed-up QA resources could focus on exploratory testing and new feature validation instead of repetitive regression work.
Magellan Health: Workday Implementation
Magellan Health’s Workday implementation showed similar results. Their regression testing costs dropped by 70%. SME involvement decreased by 80%. They saved four weeks per update cycle. When you’re running quarterly updates, that’s 16 weeks per year returned to productive work instead of regression testing.
Quantitative Outcomes
Effective regression testing delivers:
- Reduced testing cycles – From weeks or months to days or hours through automation
- Lower defect escape rates – Catching 90%+ of regressions in testing instead of production
- Cost savings – 50-80% reduction in testing costs through reusable automation assets
- Faster release velocity – Enabling frequent deployments without quality compromise
- ROI realization – Typical payback in 7-14 months, with 548% five-year ROI
- Resource optimization – Freeing QA teams from repetitive manual work to focus on high-value testing
Beyond the numbers, effective regression testing builds organizational confidence. Business stakeholders trust that updates won’t disrupt operations. Development teams iterate faster knowing that automated suites will catch regressions. Operations teams sleep better knowing that production stability is protected.
When implementing a robust SAP regression testing strategy, the right test management platform makes all the difference between costly delays and smooth releases. aqua cloud stands out as a purpose-built solution that addresses the core challenges of SAP testing. With aqua, your team can build and maintain a living test repository that evolves alongside your SAP landscape, ensuring regression coverage stays current with each update, enhancement, or S/4HANA migration. The platform’s powerful reporting capabilities provide real-time visibility into test coverage and execution status, enabling stakeholders to make confident release decisions. aqua’s domain-trained AI Copilot learns from your project’s documentation to generate contextually relevant test cases that truly understand your SAP processes, configurations, and custom code. Integration with Jira, Azure DevOps, and CI/CD pipelines ensures your regression testing fits seamlessly into your delivery workflow. Like the success stories mentioned earlier, aqua customers typically achieve 80-90% reduction in testing cycles while dramatically improving defect detection rates.
Transform your SAP regression testing from a bottleneck into a business enabler with aqua's intelligent test management platform.
Conclusion
SAP regression testing protects operational stability while you innovate. Every change in SAP carries risk of unintended consequences. Organizations that invest in comprehensive regression testing strategies release updates faster, reduce costs, and prevent production failures. The ROI is compelling: seven-month payback periods, 548% five-year returns, and 50-80% cost reductions. As SAP landscapes evolve toward S/4HANA, cloud deployments, and continuous delivery models, the need for automated regression testing intensifies. Define clear scope and impact analysis for every change. Prioritize automation for high-value, repeatable scenarios. Maintain a living test repository that evolves with your system. Integrate testing into CI/CD pipelines for continuous validation. Learn more about building a testing strategy that scales with your SAP environment. The organizations winning at SAP quality have the smartest testing strategies backed by automation and relentless focus on business-critical processes.